Did you know that by 2025, 3D printing could contribute $1 trillion to the global economy? This technology is at the forefront of the new industrial revolution, transforming how businesses operate. 3D printing is being used by businesses to produce customized goods at a faster and cheaper rate than ever before. It’s not just about prototyping anymore; it’s about real profits and art.
Embracing this innovation opens doors to endless possibilities in manufacturing, design, art, and even healthcare. From reducing waste to speeding up production times, 3D printing is changing the game. Businesses that adapt will thrive, while those that don’t may fall behind. Discover how you can profit from this groundbreaking technology and stay ahead in a rapidly evolving market. Key Takeaways Understand how 3D printing is changing industries by learning its key roles and benefits to stay competitive.
Explore various applications of 3D printing, from healthcare to automotive, to identify opportunities for innovation in your business. Keep an eye on future trends in 3D printing technology to adapt and position your business for growth. Implement strategies discussed in the article, like investing in training and partnerships, to maximize profits from 3D printing. Utilize 3D solutions to enhance efficiency in your operations, reducing waste and improving production speed. Leverage customization options offered by 3D printing to meet customer needs and stand out in the market.

Understanding 3D Printing’s Role in Industry Definition of 3D Printing Digital files are used to create three-dimensional objects using 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing. This technology builds items layer by layer. It uses materials like plastic, metal, and resin. The ability of 3D printing to change the way products are made is what makes it important. It speeds up prototyping and cuts down on waste when compared to conventional methods. Transition to Large-Scale Production Initially, 3D printing focused on creating prototypes. Designers used it to test concepts quickly.
Over time, the technology evolved. Now, it supports large-scale production in various industries. Using 3D printers, for instance, businesses can produce thousands of parts. This shift enables businesses to respond faster to market demands. Impact on Traditional Manufacturing 3D printing disrupts traditional manufacturing methods significantly. Conventional processes often require molds and extensive machinery. These methods can be costly and time-consuming. In contrast, 3D printing reduces these needs. It lowers production costs and shortens lead times. Design freedom is now greater for businesses. For instance, this technology has a significant impact on the automobile industry. Manufacturers can create complex components that were impossible with traditional methods. Additionally, aerospace companies use 3D printing for lightweight components that boost fuel economy. The design industry sees a similar impact. Designers can experiment with intricate shapes without worrying about production constraints. This freedom fosters innovation and creativity.
The Benefits of 3D Printing Cost Efficiency: Reduces material waste. Customization: Allows unique designs for specific needs. Speed:
Accelerates the production process. Accessibility: Makes manufacturing possible for small businesses. Challenges in Adoption Despite its advantages, challenges exist in adopting 3D printing across industries: Quality Control: Ensuring consistent quality can be difficult. Limitations on Materials: For 3D printing, not all materials are suitable. Regulatory Issues: Compliance with industry standards is necessary. Exploring Diverse Applications of 3D Printing Healthcare Innovations Healthcare is one of the leading industries using 3D printing technology. Implants and prosthetics are made specifically for each patient by hospitals. This process allows for better fits and improved comfort. In 2018, researchers at the University of Utah printed a heart model for surgical planning.
Such applications show how 3D printing designs can enhance patient care. Companies like Organovo focus on bioprinting tissues for drug testing. They want to lessen the use of animals for testing. Their work highlights the potential for creating human tissues that mimic real organs. This innovation could change how medical research is conducted. Packaging Solutions The packaging industry also benefits from 3D printing products. Companies use this technology to create prototypes quickly. Traditional methods often take weeks, but 3D printing can cut this time down to days.
For example, Coca-Cola has explored using 3D printers to design new bottle shapes. These quick iterations help businesses adapt to market demands faster. Custom packaging solutions are possible with personal 3D printers. Brands can test various designs before mass production, saving time and resources. Art and Design Artists embrace 3D printing technology for unique creations. Artists can design complex structures that would be difficult to make by hand. For instance, artist Anouk Wipprecht uses 3D printers to create wearable art pieces. These items combine technology and fashion.
Universities also play a role in advancing art through 3D printing. Many institutions offer courses on digital fabrication techniques. Students learn how to combine traditional artistic skills with modern technology. Prototyping and Testing In a variety of industries, prototyping remains a fundamental function of 3D printing. Engineers use it for rapid prototyping of new products. They are able to test designs using this approach prior to beginning full-scale production. Companies like Tesla utilize consumer 3D printers for developing parts efficiently. Testing prototypes aids in the early detection of design flaws. This approach saves money and reduces waste in manufacturing.
It encourages innovation by allowing teams to experiment without significant costs. Customized Solutions Customization is another significant advantage of 3D printing. Businesses can produce items tailored specifically to customer needs. For example, Nike offers personalized shoe designs using 3D printing methods. Customers can choose colors, materials, and even fit preferences. Beyond consumer goods, this trend toward customization extends. Industries such as aerospace and automotive also leverage this technology for bespoke components. Each industry uses 3D printing in unique ways to meet its specific needs. Future Prospects of 3D Printing Technology: Trends on the Rise 3D printing technology is evolving rapidly.
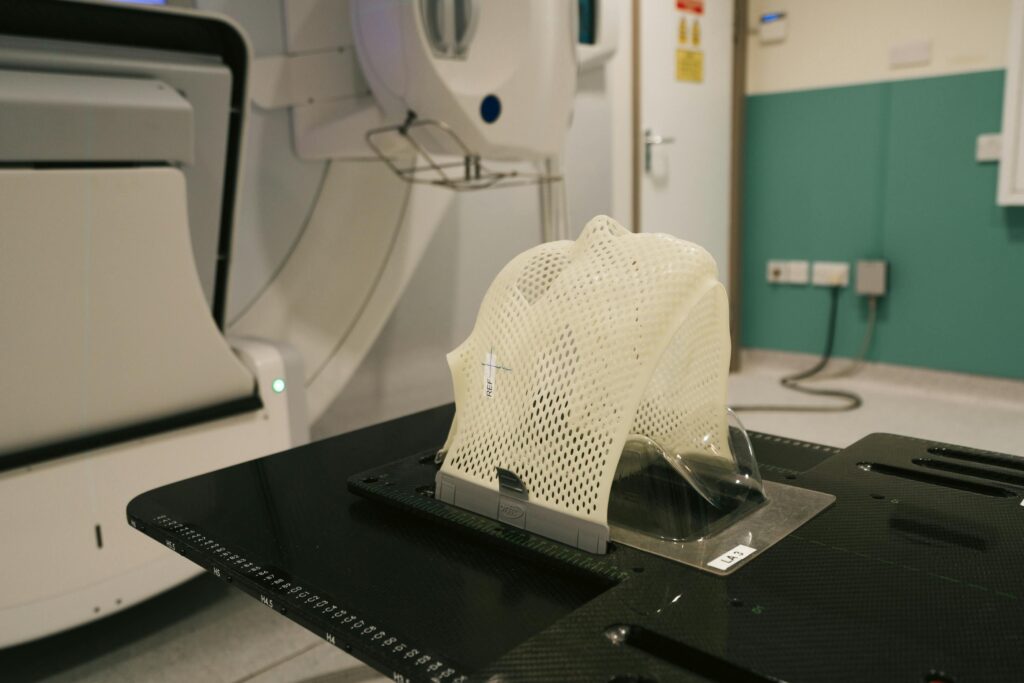
New technologies are emerging every year. These advancements improve speed, quality, and cost-efficiency. For instance, 3D printing technology has become increasingly popular in creative industries. Artists use it to create intricate designs that were once impossible to produce. In the medical field, innovations are transforming patient care. 3D printing allows for customized prosthetics. Patients can receive prosthetic options tailored to their specific needs. This personalization enhances comfort and functionality. Potential Breakthroughs Several potential breakthroughs could reshape industries. Construction is one sector. 3D printing can create entire structures with less waste and lower costs. Using this method, a company built a house in just 24 hours in 2021. Another promising area is bioprinting. Scientists aim to print human tissues and organs.
Transplant medicine could be completely transformed by this development. It may reduce the need for donors and waiting lists. The automotive industry also sees benefits from 3D printing. Manufacturers use it to produce lighter parts, improving fuel efficiency. Companies like BMW have already integrated these techniques into their production lines. Collaboration Importance For the advancement of 3D printing technology, business and educational institutions must work together.
Students learn about new technologies in schools. They get them ready for jobs in this expanding field. Partnerships allow businesses to access fresh ideas from students. Universities benefit from real-world challenges presented by companies. This teamwork fosters innovation and accelerates development. Essential are programs that emphasize hands-on experience. Internships provide students with practical skills. They design models and