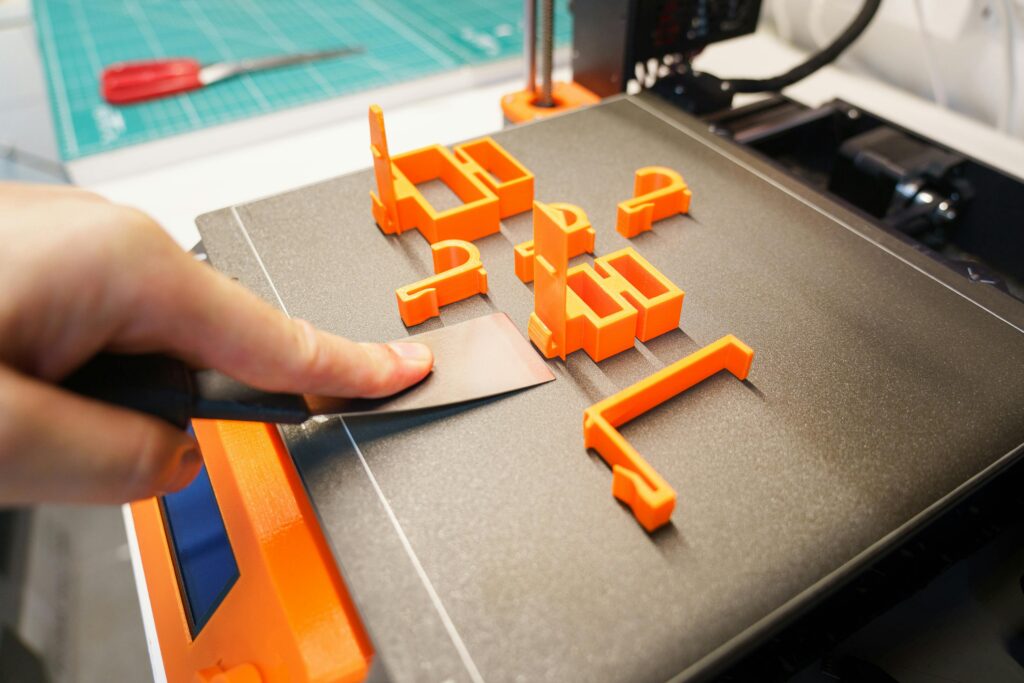
A type of rapid prototyping technology known as additive manufacturing (AM) is 3D printing (3DP). It is a technology that uses powdered metal or plastic and other adhesive materials to construct objects layer by layer based on digital model files.
To be exact, one of many rapid prototyping technologies is 3D rapid prototyping. Rapid Prototyping Technology can be roughly divided into 7 categories, including 3D printing, layered solid manufacturing, selective laser sintering, fusion deposition forming, 3D welding, 3D printing, digital accumulation forming. Digital material printers are typically used to perform 3D printing.
It is commonly used in mold manufacturing and industrial design fields to produce models and has gradually been used for direct manufacturing of some products. This technology’s printed parts are already in use. The technology has been applied in jewelry, footwear, industrial design, architecture, construction (AEC), automotive, aerospace, dental and medical industries, education, geographic information systems, civil engineering, firearms, and other fields.
Following the guidelines of the design files, the 3D laser printer first sprays solid powder or molten liquid material to solidify into special flat layers. After the first layer is solidified, the 3D laser printer head returns to form another thin layer outside the first layer. After the second layer is solidified, the printer head returns again to form another thin layer outside the second layer.
Repeat this process and ultimately stack thin layers into 3D objects. Unlike traditional manufacturing machines that create objects using cutting or molding, 3D laser printer forms physical objects by stacking layers, expanding the scope of digital concepts from a physical perspective. The 3D laser printer is a preferred processing device for precisely forming internal grooves or interlocking parts in the real world. Printing models with high accuracy naturally results in excellent quality. In addition to the design on the contour curve, the structure and movement components are not a problem. 3D printing has brought a manufacturing revolution worldwide. In the past, component design was entirely dependent on whether the production process could achieve it.

The emergence of 3D laser printer will overturn this production idea, enabling companies to produce components without considering the production process. Any complex shape design can be achieved through 3D laser printing. 3D printing can directly generate objects of any shape from computer graphic data without the need for machining or molds, greatly reducing production cycle times and increasing production efficiency. The technology of 3D printing has enormous market potential and will undoubtedly become one of many breakthroughs in manufacturing in the future, even though it still needs to be perfected. PREV: JLCPCB and Uniontech Join Hands to Deepen the Plough of Electronics Industry Next: The World of the Chinese Legendary and Monstrous Ancient Book The Classic of Mountains and Seas Is Perfectly Recreated Using 3D Printing Technology The nature of 3D Printing, a rapid prototyping technology known as a significant symbol of the third industrial revolution, is additive manufacturing (AM). In recent years, 3D printing technology has flourished both inside and outside of China, and has been widely used in aerospace, biological and medical engineering, industrial manufacturing and many other industries. Though China was late in developing 3D printing, it is the biggest potential market for 3D printing and is expected to grow faster than the global market. UnionTech, which was established in 2000, was one of the earliest businesses in China to engage in 3D printing and the first to successfully transform 3D printing for commercial purposes from a laboratory process.
It has been involved in and witnessed the major development course of the 3D printing industry in China. With its own self-developed and self-produced ultraviolet SLA 3D printer, UnionTech officially entered the 3D printing market at the start of its existence. It took UnionTech only 4 years to expand its business into overseas and to cover the global market. Currently, it owns over 60% SLA 3D printing customers in the industrial field in China and serves as an iconic symbol of industrial 3D printing in China. The early development of 3D printing in China was affected by the market and application circumstances. In the face of a low market acceptance to 3D printing, General Manager Ma Jinsong, who has marketing background and great sensitivity to the market, believed that the expansion of 3D printing market depends not on marketing approaches but upon identification and satisfaction of real customer demands, which is the only way to improve the market acceptance of 3D printing. Relying on years of application experience, UionTech has set up Industrial Application Business Division, Shoe-Making Application Business Division, Dental Application Business Division and Education Application Business Division.
It has achieved several successful cases by dedicating a lot of technical and service efforts to studying the application in various industries. For over 20 years, UnionTech has been dedicated to developing and updating 3D printing technologies and products based on different applications, to offer the specifically desired product and tackle problems in the application chain. Industrial application, as the first application field on which UnionTech worked, could be divided into many segments, such as aerospace, automobile manufacturing, electronics, home decoration, toy production, architecture and medical treatment. Speaking of UnionTech’s tremendous contribution to the development of 3D printing in China, some of its typical applications in the industrial manufacturing sector in the past 20 years must be mentioned. Leading application drives the development of 3D printing industry Prototype As the currently largest prototype producer in Asia, Dongguan FOHAN started to buy UnionTech products when UnionTech set foot into prototype market at its early stage.
Being affected by the market and technology, 3D printing developed especially slowly in the first decade when labor force and manufacturing system began to change. In an interview, Wen Binghua, Board Chairman of FOHAN who learnt about 3D printing at the early stage, recalled that, “Since labor cost increased after 2000, prototype production heavily relying on proficient manual works run into trouble and fully revealed its biggest disadvantage. In 1997, CNC workers were paid RMB 1,000, which increased to RMB 4,000-5,000 ten years later at an average annual rate of 15%. In 2000, apprentices paid tuition fees; but now, they get paid. Senior technical workers are the best qualified to speak on technical issues. But it was difficult to find successors to them due to low salary, loud noise in the workshop and serious brain drain. Under such circumstance, many prototype producers started their transformational moves.”